Invention Reference: 11/MED/0421
Engineering of Polymer-stabilized Drug Nanoparticles by Flash Nanoprecipitation
|
The invention provides an effective and pragmatic means for controlled production of polymer-stabilized drug nanoparticles with the desired particle size and surface properties for specific biological and pharmaceutical applications. At present there are no available technologies or approaches that can widely serve this purpose. |
|
Advantages
•Ease of operation
•Good reproducibility of nanoparticles generated in the 50-200 nm size range
•Applicable to a wide range of materials
•Amenable to scale-up for industrial production |
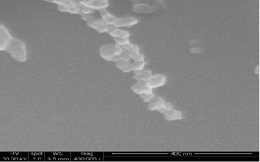
Scanning electron micrograph of nanoparticles at a magnication of 400,000 |
|
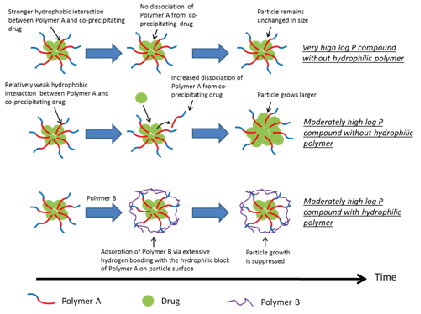
A proposed stabilization mechanism (many drugs have moderately high LogP)
|
|
Technology Description
Nanoparticles are structures with a diameter on a sub-micrometer scale. Potential advantages of nanoparticles comprised of drugs as delivery vehicles include improved absorption, site-specific targeting, reduced metabolism, lower toxicity, and enhanced efficacy. Nanoparticles may greatly enhance the transport of drugs across biological membranes, including those of the gut and the blood-brain barrier. |
 |
Flash NanoPrecipitation (FNP) is normally achieved with the aid of a specially designed mixer [e.g. confined impinging jet (CIJ) mixer or multi-inlet vortex mixer (MIVM)] in which an organic solution containing a drug and a protecting polymer is rapidly mixed with an antisolvent (water) within a time scale shorter than those of the nucleation and particle growth processes. |
|
CIJ mixer and MIVM are different in both design and mixing mechanism. For the CIJ mixer, mixing is achieved by continuous frontal collision between two high-velocity linear streams (i.e. drug solution and antisolvent) in the center of a cylindrical chamber, whereas the MIVM adopts a vortex mixing principle. In terms of operation, MIVM offers higher flexibility and mixing efficiency since it consists of four inlet streams whose flow rates can be independently adjusted. |
|
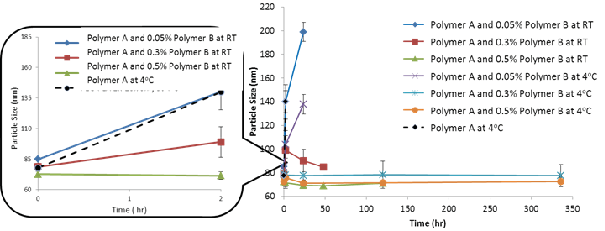
Effect of storage time on particle size for samples containing Polymer B. Note that the samples (data points) with pacticle size > 200 nm or visible preciptation are classified as failure (i.e. unstable formulation) and omitted from figure.
|
Nanoparticles of Curcumin for Treating Cancer or Infection
|
Curcumin has long been shown to exhibit therapeutic potential for treating cancer, infections and Alzheimer’s disease, however its low water solubility significantly limits its oral absorption to achieve therapeutic effectiveness.
Our novel drug formulation technique provides a pragmatic means for producing curcumin naonoparticles to address this problem.
Advantages
• Natural product
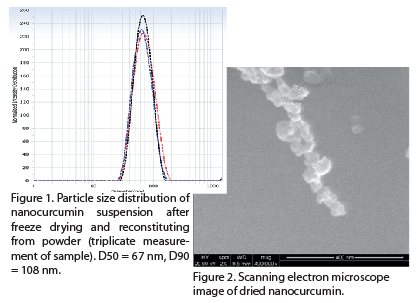
•Good reproducibility of curcumin nanoparticles in the 45-59 nm size range
• Amenable to scale-up for industrial |
|
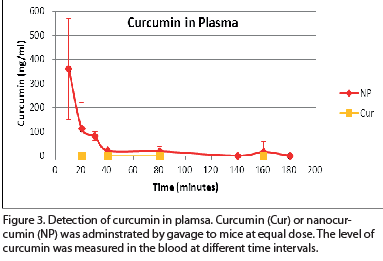
|
 |